Understanding Numbness in Legs: Expert Care in Orem and Lehi, Utah
Experiencing numbness in legs can be a concerning and uncomfortable sensation that affects many residents of Orem and Lehi, Utah. At Foundation Chiropractic, we understand how leg numbness can significantly impact your daily life and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the causes of numbness in legs, when it should be a cause for concern, and what effective treatment options are available for Utah County residents experiencing this troubling symptom.
What Causes Numbness in Legs?
Leg numbness can result from a variety of factors, ranging from minor issues to more serious medical conditions. Understanding the underlying causes can help Orem and Lehi residents determine the appropriate course of action and seek the right pain management treatment.
1. Nerve Compression and Pinched Nerve Issues
One of the most common causes of numbness in legs is nerve compression affecting the peripheral nerves. This can occur due to conditions such as:
Herniated Disc: When the cushioning between the vertebrae in the spine bulges out, it can press on nearby nerves, leading to leg numbness and tingling sensations throughout the lower extremities.
Sciatica: This condition arises when the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down the leg, becomes irritated or compressed, causing sciatica pain and numbness in legs that many Utah residents experience.
Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal can put nerve pressure on the spinal cord and peripheral nerves, resulting in numbness and tingling throughout the leg and foot.
2. Poor Circulation and Blood Flow Issues
Poor blood circulation can lead to leg numbness due to insufficient blood flow to the lower extremities. Conditions affecting Utah residents include:
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): This occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the leg become narrowed or blocked, leading to numbness, leg pain, or cramping sensations.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Blood clots in the deep veins can obstruct poor blood circulation and cause numbness or swelling in the affected leg.
3. Nerve Damage and Peripheral Neuropathy
Nerve damage from various sources can contribute to persistent numbness:
Diabetic Neuropathy: High blood sugar levels from diabetes can cause peripheral neuropathy, a medical condition where nerves are damaged, leading to chronic numbness or tingling in the leg and foot areas.
Vitamin Deficiency: Deficiencies in essential vitamins, particularly B12, can result in nerve damage and subsequent leg numbness affecting nerve function.
4. Muscle Strain and Physical Injuries
Strains or injuries to the muscles or soft tissues in the leg can sometimes lead to numbness:
Muscle Strains: Severe muscle strains or injuries can compress nearby nerves, resulting in temporary numbness and muscle weakness in the affected leg.
Leg Injuries: Trauma to the lower leg, such as fractures or sprains, can impact nerve function and lead to persistent numbness and tingling sensations.
5. Systemic Conditions Affecting Nerve Function
Certain systemic conditions can also cause leg numbness:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: While primarily affecting the hands, this condition can sometimes contribute to overall peripheral neuropathy affecting multiple areas.
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: Similar to carpal tunnel but affecting the foot and lower leg, this condition can cause foot numbness and tingling sensation.
When to Be Concerned About Numbness in Legs
While occasional leg numbness might not be a cause for alarm, there are specific situations where Orem and Lehi residents should seek medical attention. It is essential to be aware of these signs to ensure prompt and appropriate care.
1. Persistent or Chronic Numbness
If the numbness in your legs is persistent, severe, or worsening over time, it may indicate a more serious underlying medical condition. Chronic numbness should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the cause and appropriate pain management treatment.
2. Accompanied by Other Symptoms
If leg numbness is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as:
Weakness or Muscle Weakness: Difficulty moving the leg or loss of muscle strength could indicate significant nerve damage or spinal cord issues requiring immediate attention.
Pain or Swelling: Severe leg pain, hip pain, foot pain, shoulder pain, or neck pain along with swelling may suggest conditions like deep vein thrombosis or infection.
Difficulty Walking: Trouble walking or maintaining balance can be a sign of a neurological problem affecting nerve function in the lower extremities.
3. Recent Injury or Trauma
If you have recently experienced an injury or trauma to the leg, and numbness persists, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation to rule out fractures, nerve damage, or other complications affecting the affected limb.
What to Do If You Experience Numbness in Legs
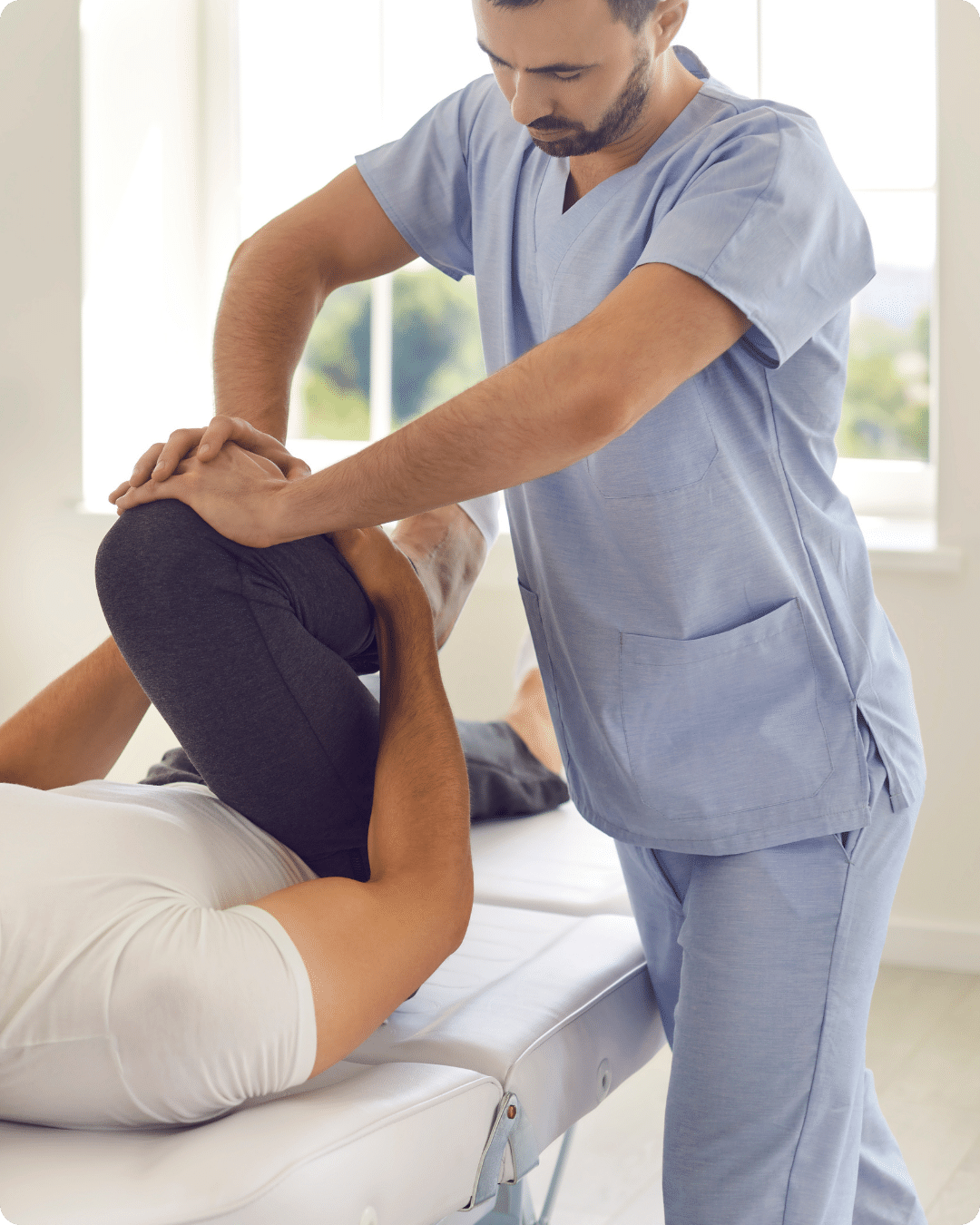

If you experience leg numbness, taking appropriate steps can help manage the symptom and address any underlying issues affecting Utah County residents.
1. Consult a Healthcare Professional
The first step is to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation. A thorough examination can help identify whether your leg numbness stems from nerve compression, poor circulation, or other medical conditions requiring specific treatment.
2. Consider Specialized Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care can be highly beneficial for addressing numbness in legs, particularly if it is related to nerve compression or spinal issues. Our chiropractors at Foundation Chiropractic in Orem and Lehi use non-invasive techniques, such as spinal adjustments and physical therapy, to alleviate pressure on nerves and improve overall nerve function.
3. Adopt Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support overall leg health and potentially reduce numbness:
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve blood circulation, strengthen muscles, and support healthy nerve function throughout the leg and foot.
Balanced Diet: Eating a nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help manage conditions like diabetes and support optimal nerve function while preventing vitamin deficiency.
Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining proper blood circulation and can help prevent muscle cramps and weakness.
4. Manage Underlying Medical Conditions
If the leg numbness is related to an underlying condition, such as diabetes or poor blood circulation, managing that medical condition is crucial. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and lifestyle changes to address the root cause of the numbness and tingling.
Our Comprehensive Treatment Approach
At Foundation Chiropractic, we offer specialized care for patients experiencing leg numbness and related symptoms:
Advanced Diagnostic Evaluation
We perform thorough examinations to identify the source of your leg numbness, whether it stems from nerve compression, peripheral neuropathy, or other underlying causes affecting sensation in your leg and foot.
Targeted Physical Therapy
Our physical therapy programs are designed to address nerve pain, improve blood circulation, and restore proper nerve function while reducing tingling and numbness throughout the lower extremities.
Pain Management Solutions
We provide comprehensive pain management strategies that address not only leg numbness but also associated symptoms like leg pain, foot numbness, and tingling sensations without relying solely on medication.
Specialized Nerve Treatment
Our treatment protocols specifically target nerve damage and peripheral neuropathy, helping to restore sensation and reduce chronic numbness affecting your quality of life.

Key Takeaways
Numbness in legs can arise from various causes, ranging from nerve compression to systemic conditions like diabetic neuropathy. Understanding the potential causes, knowing when to seek medical attention, and taking appropriate steps can help manage and address this troubling symptom effectively. At Foundation Chiropractic in Orem and Lehi, Utah, we are dedicated to providing compassionate care and support for individuals experiencing leg numbness, tingling, and related nerve pain. If you have concerns about persistent numbness, numb leg sensations, or need assistance with pain management, please do not hesitate to reach out to our experienced team for personalized care and guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What conditions can cause numbness in legs?
Leg numbness can result from various conditions including nerve compression, peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, poor blood circulation, spinal stenosis, pinched nerve issues, and nerve damage. Our team evaluates each patient to determine the specific cause of their leg numbness and tingling sensations.
How is leg numbness diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive examination including assessment of nerve function, evaluation of sensation in the leg and foot, review of symptoms like tingling and weakness, and potentially imaging studies to identify nerve compression or other medical conditions causing the numbness.
What treatments are available for persistent numbness?
Treatment options include physical therapy to improve nerve function, pain management techniques, chiropractic adjustments to relieve nerve pressure, lifestyle modifications to improve blood circulation, and management of underlying conditions like diabetes that may contribute to peripheral neuropathy.
When should I seek treatment for leg numbness?
You should seek treatment if you experience chronic numbness, persistent numbness that worsens over time, leg numbness accompanied by weakness or severe pain, or if the numbness interferes with daily activities. Early intervention can prevent progression of nerve damage and improve outcomes.
Can diabetes cause numbness in legs?
Yes, diabetes can cause diabetic neuropathy, a type of peripheral neuropathy that commonly affects the leg and foot. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to numbness, tingling sensation, and nerve pain in the lower extremities. Proper diabetes management is essential for preventing further nerve damage.
