Understanding Leg Length Discrepancy: Causes, Measurement, and Solutions
Leg length discrepancy (LLD) refers to a condition where one leg is shorter than the other, leading to uneven leg lengths. While this can be as minor as a few millimeters or as significant as several centimeters, even slight differences can affect a person’s posture, gait, and overall physical health. LLD can arise from congenital factors, injury, or conditions like hip dysplasia. Another cause is the natural growth imbalance that may occur during childhood or adolescence, where one leg grows faster than the other. Over time, these discrepancies may lead to discomfort or chronic issues such as lower back pain, hip problems, or knee pain, which occur due to the body’s misalignment. Identifying leg length discrepancy early is important to prevent these long-term effects and can be done using several methods that range from simple visual assessments to more precise imaging techniques.
Measuring Leg Length Discrepancy
Measuring leg length discrepancy (LLD) is crucial for both accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. One of the most common ways to assess LLD is through a physical examination, where a doctor visually compares the legs while the patient is standing or lying down. This initial observation helps determine if there is an obvious difference in leg lengths. Another method involves measuring the distance from the anterior superior iliac spine (a bony prominence near the hip) to the medial malleolus (the inner side of the ankle). This simple but effective technique can be done by a healthcare provider or even at home with proper guidance.
For more accurate results, especially in cases where the discrepancy is significant or surgical intervention is being considered, advanced imaging tools such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans may be used. These imaging techniques not only confirm the presence of LLD but also help determine if the discrepancy is structural (due to actual bone length differences) or functional, where the legs appear unequal because of issues with the pelvis, hips, or spine. Functional LLD may require different treatment strategies, such as adjustments in posture or gait, compared to structural LLD.
Accurately diagnosing the type and degree of LLD is essential for creating a customized treatment plan. This plan could include non-invasive treatments like exercises or physical therapy to improve muscle strength and flexibility, shoe lifts to compensate for minor discrepancies, or in severe cases, surgical options like bone lengthening or shortening. Identifying and addressing LLD early on can significantly improve a person’s mobility, comfort, and quality of life.
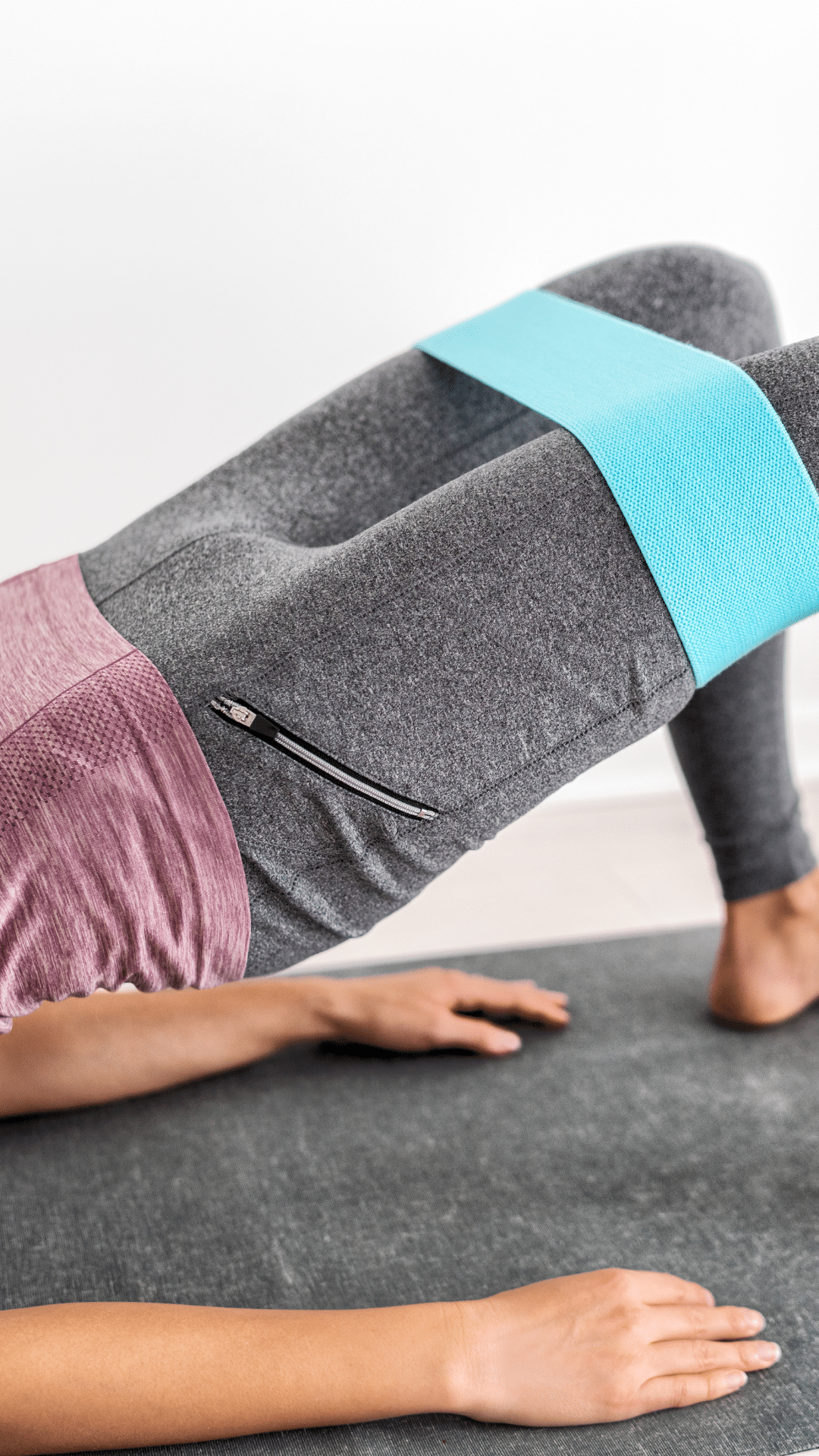

Exercises for Leg Length Discrepancy
Exercises for leg length discrepancy (LLD) play an important role in alleviating discomfort and correcting muscle imbalances caused by the condition. By strengthening the muscles around the hips, lower back, and legs, these exercises can improve balance and promote better overall body alignment. One highly effective exercise is the hip bridge, which targets the gluteal muscles and helps stabilize the pelvis. To perform a hip bridge, lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground. Lift your hips off the floor, engaging your glutes and keeping your core tight. Hold this position for a few seconds before lowering back down. This exercise helps in maintaining pelvic stability, which is crucial for compensating for uneven leg lengths.
Another valuable exercise for LLD is the lunge, which targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes while improving lower body strength and flexibility. To perform a lunge, step forward with one leg and lower your body until both knees form 90-degree angles, ensuring your front knee doesn’t extend past your toes. This exercise not only strengthens leg muscles but also enhances flexibility and mobility, both of which are essential for managing the effects of LLD.
Stretching exercises also play an important role, particularly for the hamstrings and hip flexors. Stretching these muscles can reduce tightness and improve the range of motion in the hips and legs, easing tension caused by the imbalance. For example, hamstring stretches can be performed by sitting on the floor with legs extended and gently reaching toward the toes. Regular stretching helps maintain flexibility and reduces the likelihood of joint pain caused by LLD.
While these exercises won’t physically change the length of the legs, they can help manage the imbalances and discomfort by promoting better alignment and muscle function. In more severe cases, where exercises alone are insufficient, physical therapy might involve the use of custom orthotics or shoe lifts. These devices help to balance leg length discrepancies, reduce strain on the lower back and joints, and improve posture, ultimately providing a comprehensive approach to managing LLD
How Leg Length Discrepancy Can Affect Physical Activties
Leg length discrepancy (LLD) can also impact athletic performance and physical activities. Individuals with LLD may find it challenging to engage in sports or exercises that require balance, coordination, or repetitive motion, such as running or cycling. The uneven leg lengths can cause altered biomechanics, leading to overuse injuries in one leg, foot, or even the spine. Athletes may experience muscle fatigue or strains more frequently, especially if the discrepancy goes unnoticed or untreated. Incorporating shoe lifts or orthotics into footwear can help to correct these imbalances, allowing for more even weight distribution and improved performance. Addressing LLD through proper diagnosis and treatment can be crucial for maintaining long-term joint health and preventing further complications.
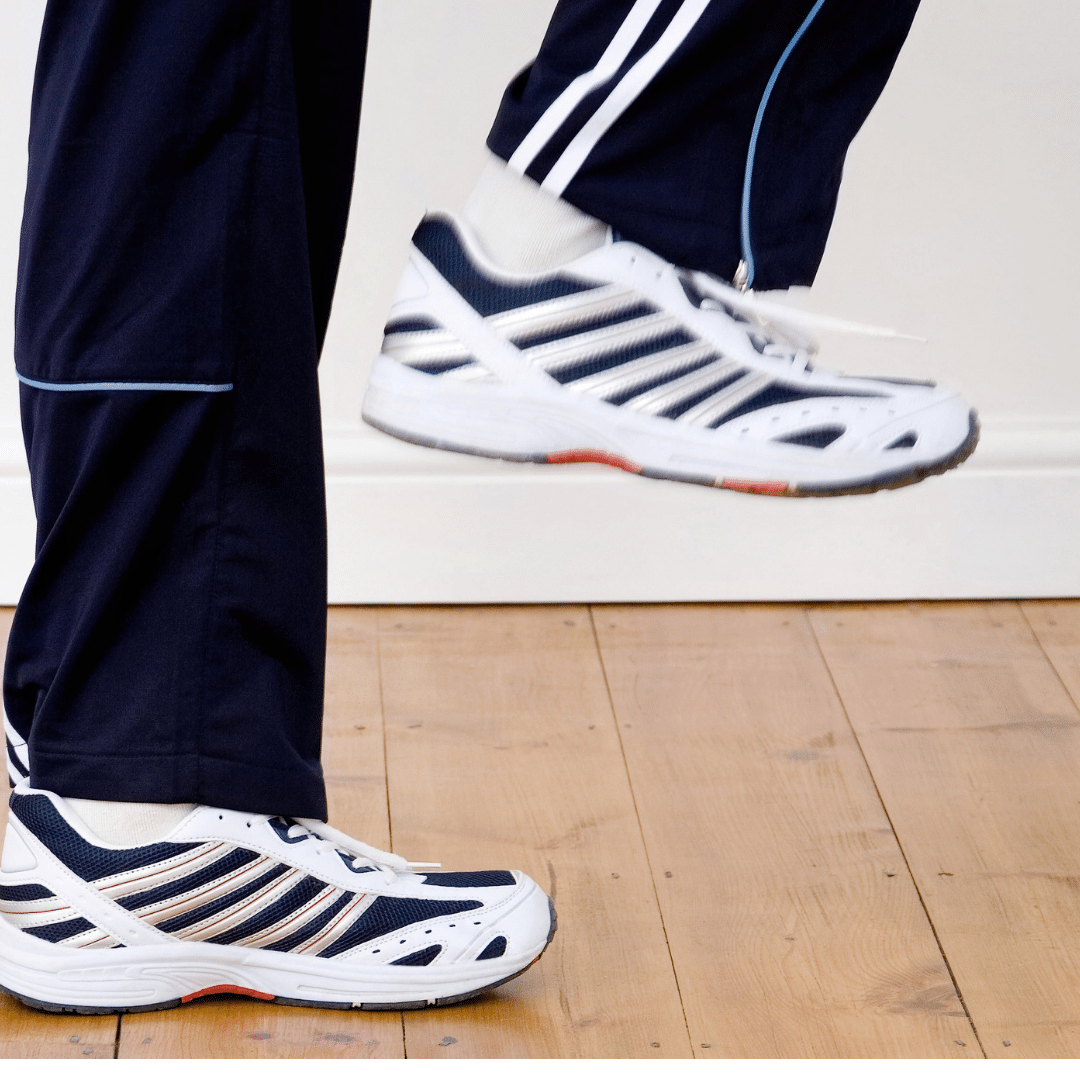

Final Thoughts On Leg Length Discrepancy
In summary, leg length discrepancy can affect various aspects of physical health, but early detection and targeted treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications. Whether it’s through measuring techniques, tailored exercises, or supportive devices, addressing leg length differences is crucial for maintaining alignment and mobility.
How to Exercise While Sitting FAQs
What are the common symptoms of leg length discrepancy (LLD)?
Common symptoms of LLD include uneven gait, hip, knee, or lower back pain, and noticeable posture issues such as leaning to one side. Over time, these symptoms can lead to more serious issues like arthritis or joint problems if left untreated.
How is leg length discrepancy diagnosed?
LLD is typically diagnosed through a physical exam where a doctor compares the legs visually or measures from the hip to the ankle. More precise methods include imaging techniques like X-rays or MRI scans, which can measure the difference in leg length and detect any underlying issues.
Can leg length discrepancy be corrected without surgery?
Yes, mild to moderate cases of LLD can often be managed with non-surgical treatments like custom orthotics or shoe lifts, exercises to improve muscle strength and balance, and physical therapy. Surgery may only be recommended for severe cases where the leg length difference significantly impacts daily activities.
Is leg length discrepancy common in children?
Yes, LLD can occur in children, often due to natural growth imbalances where one leg grows faster than the other. It can also be caused by congenital conditions, injuries, or medical conditions affecting bone growth. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent future complications.
